
Stepper motors are a simple and cost-effective solution for
applications that do not require position feedback and operate exclusively within the design limits of the
motor
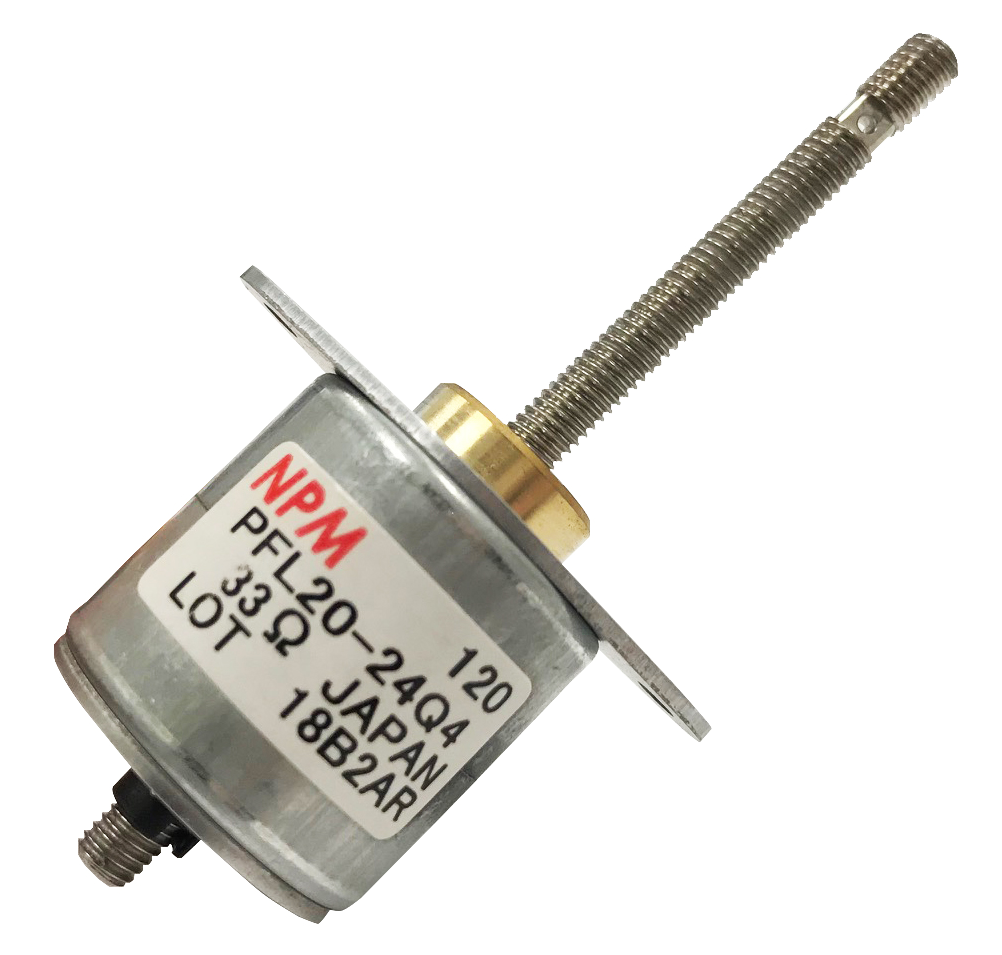
Linear stepper motor with 20 mm diameter
offers 8 Nm torque
Nippon Pulse permanent magnet (PM) stepper motors (PF series Tin-Can stepper motors) are firmly established in
mechanical engineering and offer many advantages over other types of stepper motors. They have an excellent
price-performance ratio and are suitable as a low-inertia, low-resolution, low-cost alternative to hybrid
stepper motors in many applications.
As a simple motion system, the PFL (LINEARSTEP®) series of linear Tin-Can stepper motors are available at a fraction of the cost of a conventional rotary stepper motor. The LINEARSTEP® series (distributed by Dynetics) has now been supplemented with a 20-millimetre diameter.Simple structure,
The PFL20-24Q4 has a thread pitch of 0.05 mm/step (1.2 mm/rev) and is available with bipolar winding. The usable
stroke is between 0 to 30 mm and the maximum torque is 8 Nm. The PFL20 is RoHS compliant, has an effective
stroke of 30/60 mm and can reach a force of 6 N at 200 pps. With 24 steps per revolution, the lead screw has a
thread pitch of 1.2 mm. The PM stepper motor also achieves a rated voltage of 5 V, a resistance of 33 ohms/phase
and an inductance of 12 mH/phase.
The simple structure of LINEARSTEP® motors – just a threaded rotor hub and lead screw – helps save space and reduce costs by requiring fewer components than systems that convert rotary motion into linear motion.
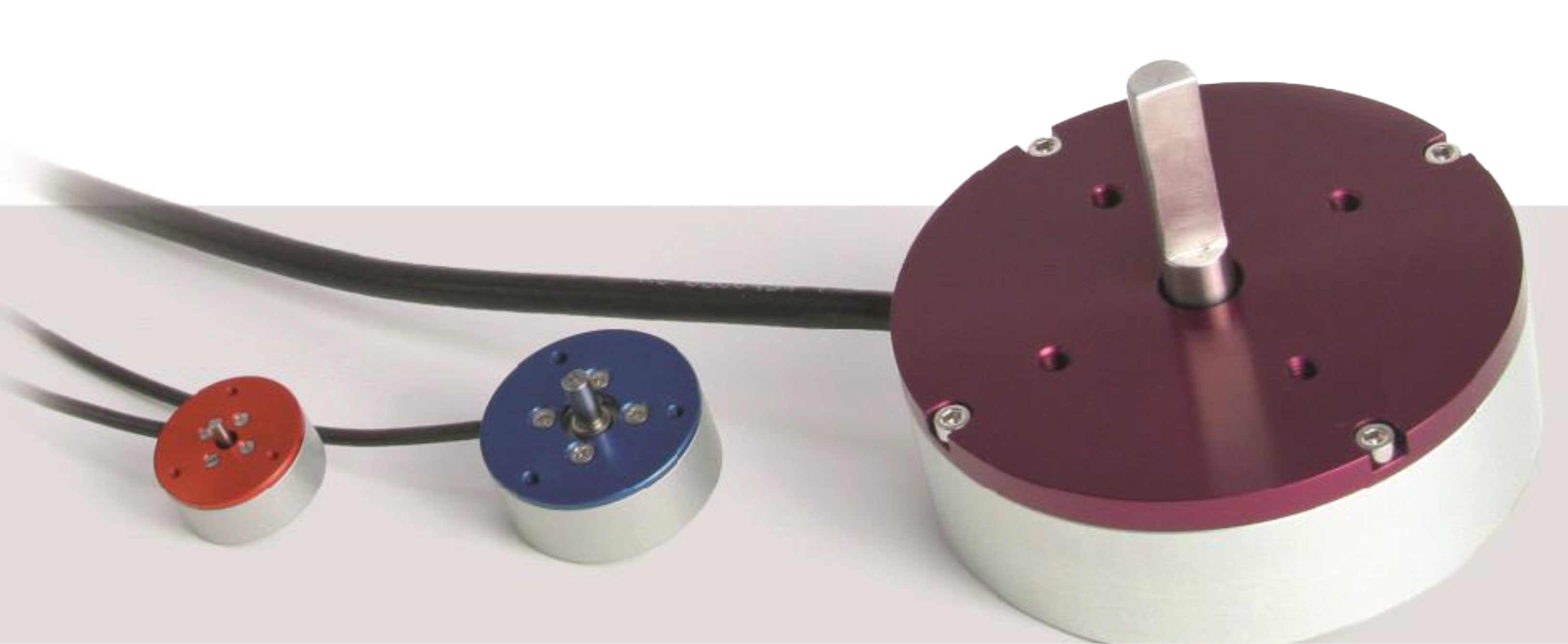
LINEARSTEP® motors are also easy to control and can be ordered with unipolar or bipolar windings and a variety of voltages. In addition to the 20 mm motor size, this motor is also available in 25 mm (with or without latch) and 35 mm diameter sizes. Customisation of Tin-Can linear actuators, including the LINEARSTEP®, is possible.
 Overview LINEARSTEP® series
Overview LINEARSTEP® series
 Video: Syringe captive vs hybrid2
Video: Syringe captive vs hybrid2
As a simple motion system, the PFL (LINEARSTEP®) series of linear Tin-Can stepper motors are available at a fraction of the cost of a conventional rotary stepper motor. The LINEARSTEP® series (distributed by Dynetics) has now been supplemented with a 20-millimetre diameter.
Simple structure,
high performance
The PFL20-24Q4 has a thread pitch of 0.05 mm/step (1.2 mm/rev) and is available with bipolar winding. The usable
stroke is between 0 to 30 mm and the maximum torque is 8 Nm. The PFL20 is RoHS compliant, has an effective
stroke of 30/60 mm and can reach a force of 6 N at 200 pps. With 24 steps per revolution, the lead screw has a
thread pitch of 1.2 mm. The PM stepper motor also achieves a rated voltage of 5 V, a resistance of 33 ohms/phase
and an inductance of 12 mH/phase.The simple structure of LINEARSTEP® motors – just a threaded rotor hub and lead screw – helps save space and reduce costs by requiring fewer components than systems that convert rotary motion into linear motion.
LINEARSTEP® motors are also easy to control and can be ordered with unipolar or bipolar windings and a variety of voltages. In addition to the 20 mm motor size, this motor is also available in 25 mm (with or without latch) and 35 mm diameter sizes. Customisation of Tin-Can linear actuators, including the LINEARSTEP®, is possible.

