The decisive factors for the efficiency, volume flow, service life and noise level of fans and blowers are
the
motor, material and the aerodynamic design of the components.
When selecting a fan or blower, the required air flow and the ventilation resistance of the units must be
determined. The exact determination of a ventilation resistance is however difficult. Generally, you can
select
the maximum airflow of a fan by multiplying the required airflow by 1.3 to 1.5.
If an adequate air channel is not available due to a high density of mounted parts, a fan with a maximum
airflow
of more than twice the required airflow is sometimes needed. In this case, a special fan for a high static
pressure range or a blower is recommended.
DC fans and blowers have the following relationship between the applied voltage and the PQ characteristics.
The
speeds of fans and blowers are proportional to the applied voltage. By varying the voltage by ±10 percent,
the
speed changes by ±10 percent. The speed determines the static pressure and the air flow as follows: The
static
pressure correlates with the square of the fan speed and the air flow in relation to the speed. A change in
voltage of ±10 percent causes the maximum static pressure to vary by -19 to +21 percent and the maximum
airflow
to vary by ±10 percent.
Optimized product development
with CFD analysis
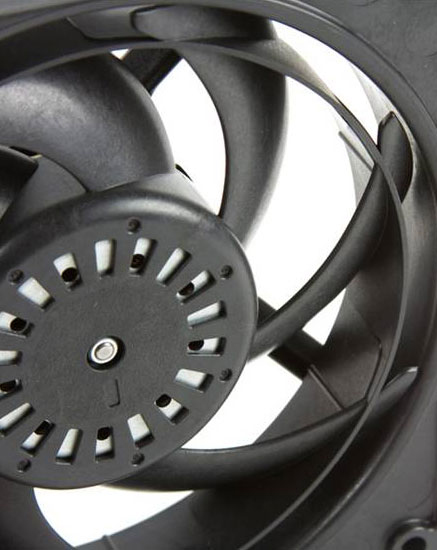
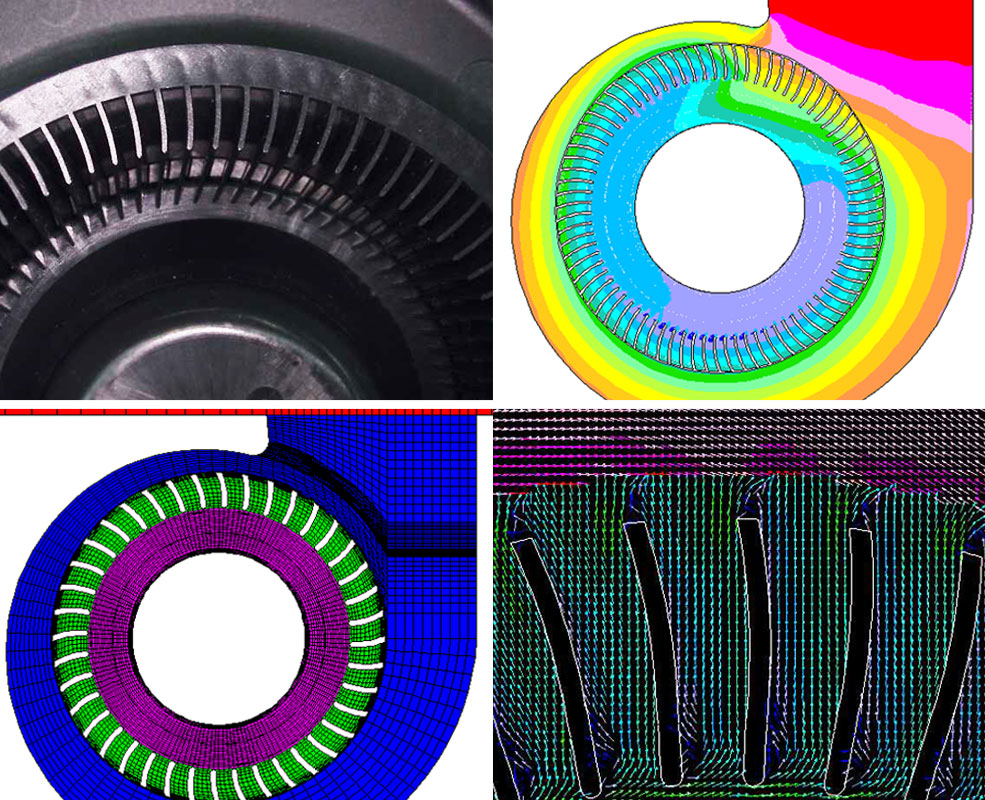
The contours of the fan blade are complicated, three-dimensional shapes. Nidec Servo is studying the flow
behavior of fan blades in special laboratories to develop quieter fans with higher efficiency. For product
development, the manufacturer uses CFD analysis software (CFD: Computational Fluid Dynamics).
CFD is the innovative design technology of fan blades which allows the realization of low-noise rotor
cascades.
The special shape of the fan blades leads not only to a better air flow, but also to a significantly lower
noise
level. Using this process, Nidec Servo has developed its radial and axial fans for the highest performance
requirements in many specific applications.
Fan blades made of polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) prevent deformation at high speed and
temperature. For highly static pressure applications, diagonal fans (which emit air in centrifugal direction) or two
axial
fans mounted in series are used. However, these solutions have disadvantages in terms of efficiency
(airflow,
size and cost) and noise.
Fan blades made of polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) prevent deformation at
high speed and temperature
Significantly lower noise emission and energy savings
The noise emission of fans has various causes. One distinguishes between aerodynamic noise, mechanical noise
(engine, bearing) and cavity noise. Aerodynamic noise can be classified into noise of rotation and eddy flow
sound. Noise of rotation (propeller sound) is mainly caused by the fan blades. Turbulences in the inflow
flow
cause vortex flow noises. Mechanical noise is generated by the motor, unbalances, resonances and phase
changes
during switching.