Linear motors
with direct drive
Dynetics, the specialist in
mechatronics, summarizes both the latest innovations and proven components it offers in the field of
linear motors. As is well known, direct-drive linear motors produce a linear, that is, straight-line
(translational) motion. Due to their high performance, flexibility, and efficiency – in terms of thrust,
speed, acceleration, and positioning accuracy – linear motors are suitable for a wide range of
applications. They enable rapid movements in confined spaces and are particularly well-suited for
complex motion sequences.
Linear motors
with direct drive
Dynetics, the specialist in
mechatronics, summarizes both the latest innovations and proven components it offers in the field of
linear motors. As is well known, direct-drive linear motors produce a linear, that is, straight-line
(translational) motion. Due to their high performance, flexibility, and efficiency – in terms of thrust,
speed, acceleration, and positioning accuracy – linear motors are suitable for a wide range of
applications. They enable rapid movements in confined spaces and are particularly well-suited for
complex motion sequences.


Drive Technology
For nearly every task, there is a suitable linear motor. Thanks to high linear force even at low speeds, they
are ideal for precise pushing, pulling, lifting, or tilting motions. Linear motors can be precisely tailored to
the requirements of an application and operate with exceptional efficiency. Additionally, they are characterized
by very high repeatability.
Typical areas of application include manufacturing – for example, in CNC machines, assembly robots, or 3D printers – as well as medical technology. In these fields, they are used in devices such as analyzers and pipetting robots, or for precise positioning in CT scanners, MRI machines, and the needle of surgical robots. The goal is always to select the optimal drive for the respective application in order to best utilize the advantages and possibilities of different technologies.
A linear actuator can also be realized using a combination of magnetic and mechanical drive concepts, for example by pairing a rotary motor with an integrated linear screw.
The choice depends on the specific requirements of the application. Ball screw drives are ideal for heavy-duty, high-precision applications, while linear servo motors are suitable for applications requiring speed and dynamic control.
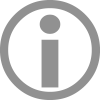 Linear Solutions
Linear Solutions
Typical areas of application include manufacturing – for example, in CNC machines, assembly robots, or 3D printers – as well as medical technology. In these fields, they are used in devices such as analyzers and pipetting robots, or for precise positioning in CT scanners, MRI machines, and the needle of surgical robots. The goal is always to select the optimal drive for the respective application in order to best utilize the advantages and possibilities of different technologies.
Subgroups and Drive Concepts
Linear drive solutions can essentially be divided into the following subgroups: magnetic drives, mechanical drives – such as those for miniature ball screw drives according to ISO standards – and combinations of magnetic and mechanical drives. With magnetic drives, the driving force is applied magnetically to the mover (also called forcer). This category includes, among others, direct-drive linear motors (cylindrical/tubular) and linear servo motors. In mechanical drives, the driving force is transmitted through a mechanical interface, such as a lead screw, ball screws, or ball screw drive.A linear actuator can also be realized using a combination of magnetic and mechanical drive concepts, for example by pairing a rotary motor with an integrated linear screw.
The choice depends on the specific requirements of the application. Ball screw drives are ideal for heavy-duty, high-precision applications, while linear servo motors are suitable for applications requiring speed and dynamic control.
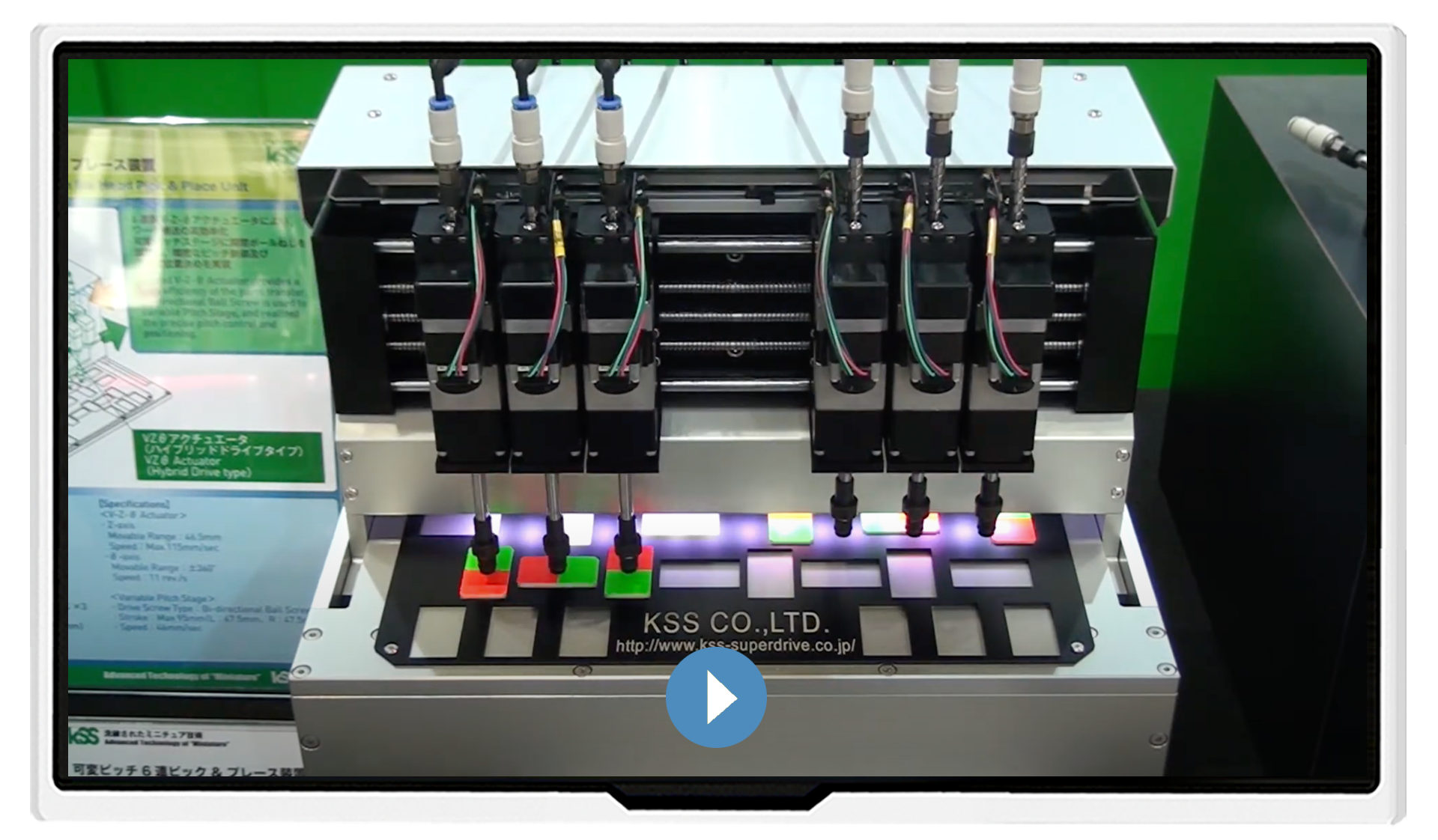
Video: Variable Pitch Stage with Six Head Pick & Place Unit
×
![]()
